The modern bee hive is like a highly efficient multistoried factory with each “story” having a specific function. These “stories” work together to provide a home for bees and a honey factory for the beekeeper.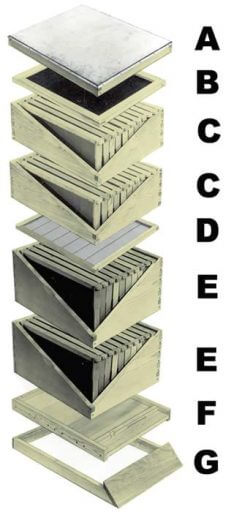
A. Hive Cover – Telescoping cover “telescopes” over the sides of the top super to protect the hive. Galvanized covering.
B. Inner Cover – Creates a dead air space for insulation from heat and cold.
C. Shallow Supers – Consist of Super, Frames and Beeswax Foundation for “surplus” honey storage. Bees store their extra honey in the frames for the beekeeper to remove. 6-5/8′ or , 5-11/16” supers, or even hive bodies may be used.
D. Queen Excluder – Keeps the queen bee in the brood chambers as she is too large to pass through the excluder. Prevents her from laying eggs and raising brood in honey supers placed above the excluder.
E. Hive Bodies – Consists of Body, Frames and Beeswax Foundation. “Brood Chambers” are the bees’ living quarters. Queen lays eggs in these chambers and brood is raised. Honey is also stored for the bees’ food.
F. Bottom Board – Forms the floor of the hive. Shown with wooden entrance reducer in place to keep mice and some cold out during winter.
G. Hive Stand – Supports the hive off the ground to keep hive bottom dry and insulate hive